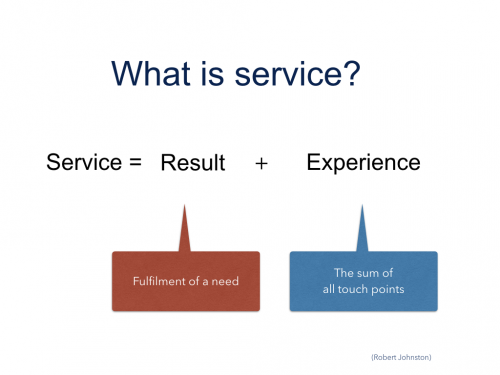
In my view, the three cornerstones in the thinking behind the concept of the Service Profit Chain are:
- Customer Loyalty – as the key objective
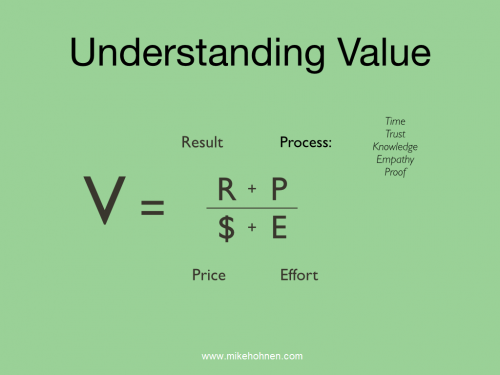
- Value – understanding the true need of the customer
- Dream Team – the people that actually make it happen
We have already looked at Loyalty and Value in the previous post.
In this post, I would like to explain the 6 key ingredients in creating a dream team:
The Right People
Careful selection of new recruits. Hire for attitude. Train for skills. Coach for performance and that includes dealing with the bad apples.
Continuous Improvement
Best in class training and development at all levels in the organization. Continuous improvement is considered one of the great benefits of the job. “In this job, I grow”…
Great Support Systems
Service is not just something the frontline does for our customers. Service is our culture. Employees and managers, who do not have customer contact, service the employees that do. (Our IT department is not the IT-Police – it is an internal service department that supports the frontline in getting the job done.)
Empowerment/autonomy
The best service employees take pride in solving the problem on the spot. So the freedom to act is hugely motivating. Southwest Airlines famously tells its employees, ”You may do anything you are not uncomfortable doing to solve a passenger’s problem.”
Clear Expectations
In the same way, that anyone who has made it to a great sports team knows what is expected of them, employees in the best service organisations also know what is expected of them. It is part of their motivation to be part of a team that is not afraid to set the bar high. Candour is a key element of high-performing teams.
Appropriate Rewards and Recognition
Focusing on what works, celebrating success, and acknowledging each other’s contributions makes work meaningful.
The principles are not complicated. There is no magic involved. But it requires commitment and persistence to get it right. When you do, the benefits are amazing.
You can download the Dream Team checklist below and benchmark yourself!
[wpdm_package id=’5519′]
This blog post is part of a series of answers to frequent questions that I get around the concept of the Service Profit Chain. In future’s posts, we will continue to explore other key points. If you would like the full concept served up in one go, you will find Mike’s book “Best! No need to be cheap if…” HERE.