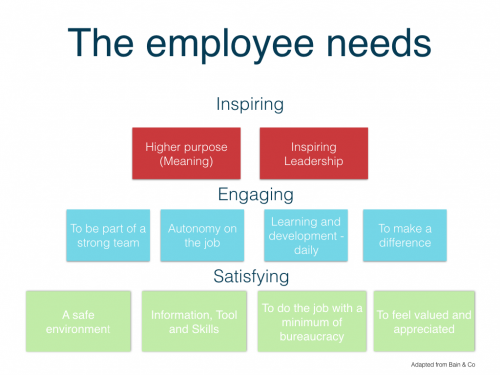
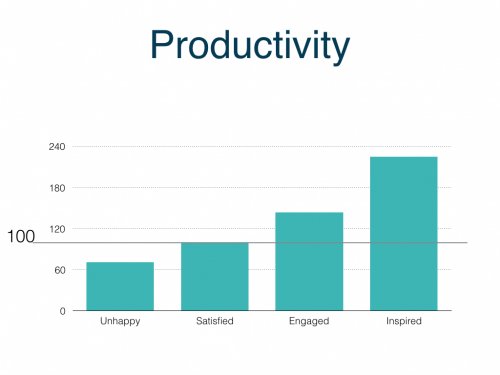
When it comes to leadership, there seems to be three major and very common challenges.
How to best:
- Provide inspiration
- Lead a team
- Develop employee capacity
During the month of October, we explored what it means to be inspirational. This month, we will explore what leadership means in a team context. December will then be dedicated to the challenge of developing employees.
Just to recap. The basic premise for this series of articles is that management and leadership are distinctly different. Both are required, but somehow we tend to focus much more on the management part of the job and tend to neglect the leadership aspect (read more about this here ). If you are in the service industry, it will ultimately affect your guest experience.
In my view, team management is all about the operational practical and very tangible aspects of what the team does. Tasks, timelines, delivery, budget and all that stuff. It all needs to be looked after or else we really get into trouble.
But good management will only get us halfway or at best two-thirds of the way to what high performance would look like.
What is a team?
Have you ever thought about what it takes for a group of people working together to transition into becoming a team?
It takes two things.
There needs to be a common goal and there needs to be a mutual responsibility for reaching that goal.
It is not enough that I do my part on the team. I must also be concerned how you are doing and if you are struggling I must do whatever I can to ensure that you are also successful with your part of the job. That is teamwork.
It’s this last part that is tricky. It is relatively easy to establish a common goal – but establishing mutual responsibility is much much harder.
In order for that to happen we need DAC – direction alignment and commitment – this is a neat concept or way of thinking about leadership developed by the Center for Creative Leadership. I have written about this before here.
Here is a simple way to evaluate if all three of these elements are happening on your team:
| Happening | Not Happening | |
| Direction | – There is a clear vision of a desired future that everyone buys into. – Team members are individually clear on what the team is trying to achieve as a whole. |
– No agreement on priorities – Team members feel they are bingo pulled in multiple directions. – There is lots of activity but not much progress. |
| Alignment | – Roles and goals are clear individually. – There is a clear understanding of how each and everyone contributes to the larger picture. – There is a sense that this is a well coordinated and synchronised effort. |
– Deadlines are missed. Rework required and lots of errors resulting in double work. – People feel disconnected from each other. – Internal competition and blame games are the norm. |
| Commitment | – Team members go the extra mile. – There is a sense of mutual understating and trust. – There are visibly high levels of engagement. |
– Only the easy things get done. – Team members are questioning what is in it for them. – Individuals avoid taking ownership and responsibility. |
If it is not happening, the obvious question is what do you need to do to make it happen? Because it’s not a management ‘thing’ – you can’t create an excel sheet or 10 point checklist – nor can you ‘tell’ them that this is what needs to happen.
What you can do, however is provide a space where they can co-create this with you. And that requires leadership.
I will come back to what you can do later in this series. Early 2017, we will launch an online training module that will show you a basic hands on approach of how to do it.
Next week, we will look at another aspect of why your team needs leadership. This has to with the instability of organic systems.
 Enter your email address below and we will notify you when we launch the Team Leader’s Toolbox!
Enter your email address below and we will notify you when we launch the Team Leader’s Toolbox!
___________________________________________________________
This post is one of a series where we are exploring the notion of leadership and how this is different from management. Our starting point is the Service Profit Chain and the understating that the management part of our job will only take us so far. If we really want to create an organisation that is capable of delivering outstanding customer experiences, we need to develop an organisation that delivers outstanding employee experiences – and that requires leadership. You can check out other articles of the series below: