
Sounds nuts, I know, but according to research by psychologist Gary Klein, it’s a great way to improve the actual outcome of your projects.
But before we go into details, there is an additional benefit that fits in with this month’s theme of improving how our top management teams function.
You see if you perform what Klein calls a pre-mortem on your projects, you are also providing a psychologically safe space for your team to voice disagreement or worries without being labelled as negative spoilsports or even worse being seen as disloyal.
So how do you do it? You make a plan for the project in your usual way, or maybe it is just a plan how you are going to execute the day with your team. When everyone is happy that we now have a plan, you announce:
“I am sorry to tell you but it has turned out that project (X) was an unprecedented disaster. Please give me your ideas as what could have happened to derail the project so badly.”
This is a very different question from asking: “So what could go wrong?” When we ask the ‘what could go wrong’ question, voicing your doubts on the team can be much trickier and often decidedly outside the psychological safety zone.
Now, everyone gets out a pad of paper and brainstorms with themselves 3-5 ways that this project could have been totally derailed, or that this day that we planned so carefully ended up a total disaster.
On a whiteboard or a flip-chart, draw a 2×2 as shown below:
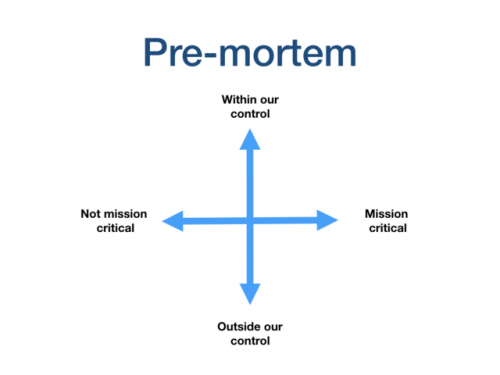
Now ask each person to read out their ideas as to why this day/ project went wrong. As they do, note the item in the appropriate square.
Now you have an overview of what problems we might encounter, sorted in a practical way. Discuss how to create proactive solutions where you can see the need and make a backup plan for the issues that you can see could happen under a certain set of circumstances.
You have now achieved two things:
1) You have proactively identified a number of issues that you would probably not have discovered until it was too late.
2) More importantly, you have provided a safe space where it is possible to actually discuss the proverbial elephant in the room. Instead of a messy feedback session loaded with blame and critique, you have made it possible to voice doubts in a constructive way regardless of hierarchies or departmental boundaries.
The method is called ‘prospective hindsight’ and according to Author Karl Weick, it can improve people’s ability to predict the reasons for future outcomes by 30%.




 We can look at the employee experience from 10.000 ft. as we have done in previous posts (
We can look at the employee experience from 10.000 ft. as we have done in previous posts (
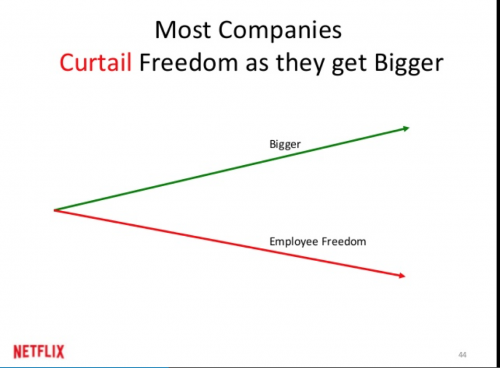

 Often teams say to me: “We need to change the culture around here.” And they often have a point, because toxic cultures are very powerful and can often destroy all sort of great initiatives – and as we have seen in a previous post, culture is a huge part of engagement. But it also easily becomes a fluffy excuse for not doing anything. It’s another drama triangle where the big villain is the culture and we are just the victims of this culture. “Well you know, that is just the culture around here. There’s not much we can do about it.”
Often teams say to me: “We need to change the culture around here.” And they often have a point, because toxic cultures are very powerful and can often destroy all sort of great initiatives – and as we have seen in a previous post, culture is a huge part of engagement. But it also easily becomes a fluffy excuse for not doing anything. It’s another drama triangle where the big villain is the culture and we are just the victims of this culture. “Well you know, that is just the culture around here. There’s not much we can do about it.”