We can look at the employee experience from 10.000 ft. as we have done in previous posts (great cultures, conversations and employee life cycle).
We can look at the employee experience from 10.000 ft. as we have done in previous posts (great cultures, conversations and employee life cycle).
Or we can go down real close up and look at the day-to-day experience.
Using the same tools and principles from Service Design thinking that we use in mapping the customer journey, we can map the employee journey over the day. When we look at it that way, a workday has three sections: Before work, work and after work. In each of the sections, we have a number of touch points related to whatever the situation is.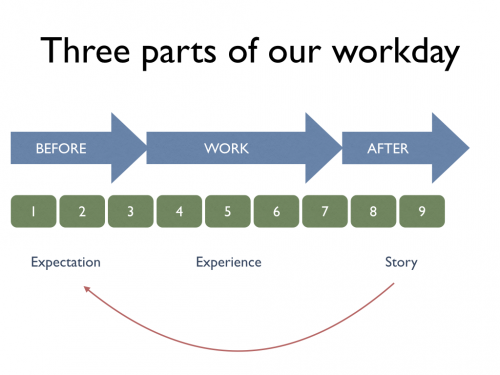
At each of the touch point, there will be 3 things going on: doing, thinking and feeling. The three elements are interdependent. Change one and it influences the other two.
Let’s begin with the end.
What happens at the end of the day? We go home for dinner or maybe off to the pub for a drink and invariably we get the question: So how was your day? And then we tell our story. Sometimes we may even feel a strong need to tell the story without anyone asking to hear it.
Our stories are interpretations.
According to Daniel Kahneman, the remembering self uses stories to make sense of the world. As soon as we experience something, we fit it into the story in our heads. What we retain from our experiences is a story.
Therefore, when we recount a memory, we’re sharing the experience of the story we created, not the actual experience.
And what defines stories?
Most of the individual moments of an experience are lost and don’t make it into the story we remember, except for changes, significant moments, and endings.
Those three key elements are what you need to be thinking about when you think through the employee journey. All three have a direct impact on their feelings.
Feelings often change as a result of shifts in our circumstances. When things go as we expect, our feelings are stable. When things go better, we are more positive and when they go worse than expected, we tend to become more negative. (Unless we are very aware of how this works and know how to deal with our own mindset, but that is a different story). The same goes for significant moments. If they are positive, they influence us in a positive way; if negative we also become negative. That endings are so important may come as a surprise to most people but it shouldn’t.
But if you think about it, when was the last time you saw a movie or read a book that had a depressing ending? There are not a lot of them around. The reason is that if you watch a movie that ends badly, you are not very likely to recommend it to your friends and family. It can be gruesome and depressing most of the time but it needs to end well otherwise you will be disappointed.
Feelings drive engagement.
So in the same way that we try and maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day by paying attention to what we eat, we should as managers be aware that maintaining stable emotional levels on our team has a lot to do with how we manage changes, significant moments and endings.
Changes in the day are inevitable, but could we reduce the impact of some of them. Be more clear in our communication or issue; heads-up warnings about things we think might happen. If we do, we make it easier for them to cope.
Significant events, some could just happen we know that but could we consciously create more positive significant events? Take five minutes to gather around the coffee machine and celebrate something. Ring a ships bell when we sign up a new client and pass around the cookie jar. There are lots of opportunities in a day to make certain moments more significant than others.
The way the day ends not only shapes how an employee perceives the whole day. How the day ends also contributes significantly to their expectations for the following day. The key question we should be asking ourselves is: do we send our people home and the end of the day in a mood where they look forward to coming back tomorrow?
A hotel head of housekeeping I have been coaching came up with a lovely way to do this. Every afternoon at 3 pm, she gathers the housekeeping team in the restaurant, serves them ‘guest-coffee’ (this was important she told me) and a pastry. They would spend the last 20 min of their shift having an informal chat about the day and how everyone feels. She tells me it has contributed to improving the relationships between them and their sense of being in this together.
What can you do to create great endings for your team members?
I would love to hear any ideas or real life examples of this if you feel like sharing, email me here.
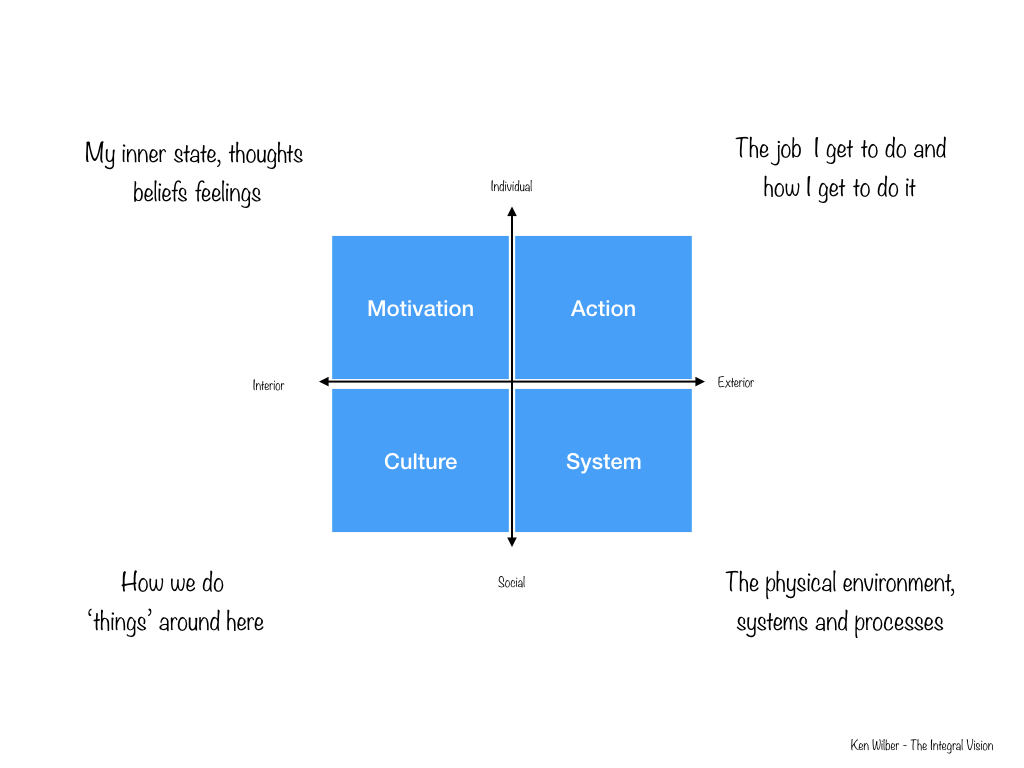

 When we design our customer experience, we typically focus on the touch points, moments of truth or my favourite moments of need. Whatever we choose to call them, these are the moments when the customer enters into contact with our service delivery system.
When we design our customer experience, we typically focus on the touch points, moments of truth or my favourite moments of need. Whatever we choose to call them, these are the moments when the customer enters into contact with our service delivery system.
 What influences how they feel?
What influences how they feel?